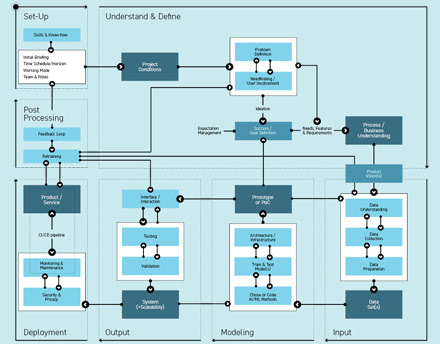
1. Problem Definition
Take the initial briefing and transform it into a problem statement. Also, try to understand if it is the right problem to solve with AI/ML.
Take the initial briefing and transform it into a problem statement. Also, try to understand if it is the right problem to solve with AI/ML.
+ Problem Statement: Translating the initial project briefing into a problem statement related to a human benefit.
+ Problem-Technology match: Using the (3) AI/ML or not checklist to see if the problem should and could be solved by an AI/ML algorithm. If the result is not to use AI/ML methods to solve the problem, this activity marks the exit point for the project.
+ Problem-Technology match: Using the (3) AI/ML or not checklist to see if the problem should and could be solved by an AI/ML algorithm. If the result is not to use AI/ML methods to solve the problem, this activity marks the exit point for the project.
2. Needfinding & User Involvement
Find out which stakeholders and users are relevant for understanding the current issues and for the final implementation. Research showed that industrial AI projects consist of a very complex network of involved stakeholders. Understanding their jobs that need to be done, pains and needs is crucial for making an informed decision about the way forward.
+ Involved Stakeholders & Users: It is crucial to understand and define who needs to be involved, also to understand their current procedures. (4) Stakeholder maps, workflow maps that visualize the status quo are a relevant tool in that regard.
+ Initial Research (qualitative): Understanding pains, problems and deriving needs. Typical methods used are (participant) observations, interviews, co creation workshops, (5) data user stories.
+ Initial Research (qualitative): Understanding pains, problems and deriving needs. Typical methods used are (participant) observations, interviews, co creation workshops, (5) data user stories.
The activities 1 and 2 are strongly related and dependent on each other. They need to go hand in hand. A clear understanding and definition of problem and user engagement are the requirements for starting ideation activities and defining success and the goal. HCD/UX designers can facilitate the conversation and lead the needfinding activities. The integration of other team members is highly recommended to create a first-hand experience.
3. Ideation
Whereas ideation and scenario development are ongoing activities throughout the whole development process, an initial ideation session based on problem definition and user stories to better align and prepare the upcoming activities should be included in this module. It can be done internally with the team or as a part of the co-creation activities with stakeholders and relevant users.
4. Success / Goal Definition
Validation item: research showed that this is a crucial action item relevant to other modules as well. When not following the whole process map, but using modules individually, it is helpful to still clarify this item.
+ Define Success Criteria/Definition of Done: Research showed that this is a highly critical step and needs to be set right from the beginning. It can be adapted during the progress of the project, but not overly stretched. It is an item that serves as a validation point during the whole project. It is not easy to agree on and a balance needs to be found between business and data science focus. Related tools are e.g. (6) confusion matrix, (7) success metrics framework, F1 score, error metrics.
Validation item: research showed that this is a crucial action item relevant to other modules as well. When not following the whole process map, but using modules individually, it is helpful to still clarify this item.
+ Define Success Criteria/Definition of Done: Research showed that this is a highly critical step and needs to be set right from the beginning. It can be adapted during the progress of the project, but not overly stretched. It is an item that serves as a validation point during the whole project. It is not easy to agree on and a balance needs to be found between business and data science focus. Related tools are e.g. (6) confusion matrix, (7) success metrics framework, F1 score, error metrics.
5. Expectation Management
Research showed that setting the right expectations is a crucial action item for AI/ML infused projects. Most of the time, expectations are wrong and too high. Implementing AI/M solutions often calls for a transformation of current processes and job routines and therefore needs to be complemented with change management activities.
Research showed that setting the right expectations is a crucial action item for AI/ML infused projects. Most of the time, expectations are wrong and too high. Implementing AI/M solutions often calls for a transformation of current processes and job routines and therefore needs to be complemented with change management activities.
+ Mental Models: Firstly, understand the mental models of the stakeholders is necessary, in order to set expectations from the start, plan and prepare for co-learning the system, as well as by the user side. Machines and algorithms with human-like behavior are not the best way to go (uncanny valley) making clear that there is a difference is a huge value add on.
+ Change Management: AI/ML is not the solution to all human problems. It is a tool that in the best case scenario, augments the human (IA - Intelligent Augmentation) to focus on the relevant aspects of his/her job. Due to fear and wrong expectations, it is necessary to embed transformation and change management activities in the project. Setting-up a role for this and raising awareness are possible activities to address this aspect.
+ Change Management: AI/ML is not the solution to all human problems. It is a tool that in the best case scenario, augments the human (IA - Intelligent Augmentation) to focus on the relevant aspects of his/her job. Due to fear and wrong expectations, it is necessary to embed transformation and change management activities in the project. Setting-up a role for this and raising awareness are possible activities to address this aspect.
6. Needs, Features & Requirements
Translating the findings from steps 1 to 5 into human needs and system requirements: (8) Analytics Use Case Canvas, (9) ML Canvas can support these activities.
Translating the findings from steps 1 to 5 into human needs and system requirements: (8) Analytics Use Case Canvas, (9) ML Canvas can support these activities.
Outcome: Process & Business Understanding
This section is heavily driven by human-centered activities informing the data-driven aspects. In this module, HCD/UX designers max out their expertise. It serves as a way to generate deeper understanding of business domain knowledge and user workflow. If this is not clear, it is necessary to start over again.